
It is simply that appearing at the previous stage.

Choose transistor: As with other forms of transistor circuit, the transistor should be chosen to meet the anticipated requirements.Directly coupled emitter follower circuit Often the collector of the previous stage will be at approximately the mid rail voltage, and this means that it can be directly coupled to the buffer stage. The simplest way of connecting an emitter follower is to directly couple the input as shown below.

Emitter follower input resistance DC coupled emitter follower, common collector circuit The input resistance can easily be calculated for a circuit because it is β times the resistor R1, where β is the forward current gain of the transistor.
As it is normally used as a buffer amplifier, this is the key parameter. One key aspect of the characteristic is the input impedance. The table below gives a summary of the major characteristics of the common collector, emitter follower transistor amplifier.Ĭommon collector, emitter follower transistor amplifier characteristics Emitter follower transistor amplifier characteristics summary Typically this is 0.6 volts for a silicon transistor and 0.2 to 0.3 for germanium transistors, although these are not widely used these days.Īs the emitter voltage follows that of the base, this means that the input and output are exactly in phase and not shifted by 180° as in the case of the common emitter amplifier. Looking at the circuit it can be seen that although the emitter voltage follows that of the base, in DC terms it is actually less than that of the base by a voltage equal to the PN junction drop between the base and emitter. Transistor common collector circuit configuration The base is connected to the previous stage, and often this may be directly connected as this can save on additional bias resistors which lower the input impedance and hence increase the loading to the previous stage. The emitter follower transistor amplifier has a very straightforward circuit. This name is derived from the fact that the emitter voltage "follows" that of the base circuit - the circuit has unit voltage gain. The other name for the common collector is emitter follower. The common collector transistor circuit configuration gains its name from the fact that the collector circuit is common to both input and output circuits, the base being associated with only the input, then the emitter with the output only.
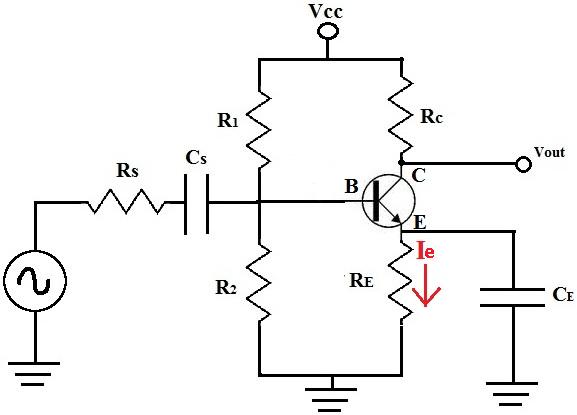
Emitter follower / common collector transistor amplifier basics The electronic circuit design for the emitter follower or common collector stage is very straightforward requiring just a few electronic components and some very simple calculations. This means that the emitter follower circuit provides an ideal buffer stage, and as a result it is used in many circuits where there is a need not to load a circuit like an oscillator or other circuit, but provide a lower impedance to the following stages. The common collector circuit configuration is more widely known as the emitter follower and it provides a high input impedance and a low output impedance. Transistor circuit design Circuit configurations Common emitter Common emitter circuit design Emitter follower Common base Transistor Circuit Design Tutorial Includes: Transistor Emitter Follower Circuit: Common Collector Amplifier The emitter follower or common collector circuit provides an ideal buffer amplifier and it is easy to design the circuit.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
